Earlier this year, a team of researchers, which included one of the 2021 study’s authors, took samples of ancient proteins preserved in the Harbin skull; of the 95 proteins they found, three of them matched proteins only encoded in Denisovan DNA. While the June 2025 study suggested that Homo longi was a Denisovan all along, the new paper draws a different conclusion: Homo longi is a species that happens to include the population we’ve been calling Denisovans. As study coauthor Xijun Ni, of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, puts it in an email to Ars Technica, “Given their similar age range, distribution areas, and available morphological data, it is likely that Denisovans belong to the Homo longi species. However, little is known about Denisovan morphology.”
Of course, that statement—that we know little about Denisovan morphology (the shapes and features of their bones)—only applies if you don’t accept the results of the June 2025 study mentioned above, which clocked the Harbin skull as a Denisovan and therefore told us what one looks like.
And Feng and his colleagues, in fact, don’t accept those results. Instead, they consider Harbin part of some other group of Homo longi, and they question the earlier study’s methods and results. “The peptide sequences from Harbin, Penghu, and other fossils are too short and provide conflicting information,” Ni tells Ars Technica. Feng and his colleagues also question the results of another study, which used mitochondrial DNA to identify Harbin as a Denisovan.
In other words, Feng and his colleagues are pretty invested in defining Homo longi as a species and Denisovans as just one sub-group of that species. But that’s hard to square with DNA data.
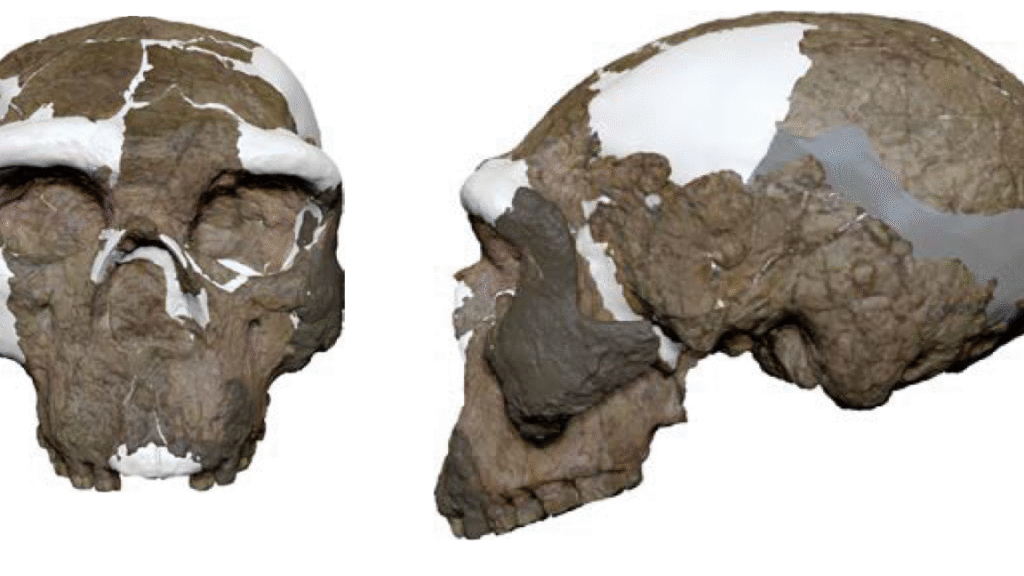
Alas, poor Yunxian 2, I knew him well
Yunxian 2 has a wide face with high, flat cheekbones, a wide nasal opening, and heavy brows. Its cranium is higher and rounder than Homo erectus (and the original reconstruction, done in the 1990s), but it’s still longer and lower than is normal for our species. Overall, it could have held about 1,143 cubic centimeters of brain, which is in the ballpark of modern people. But its shape may have left less room for the frontal lobe (the area where a lot of social skills, logic, motor skills, and executive function happen) than you’d expect in a Neanderthal or a Homo sapiens skull.
Source: arstechnica.com